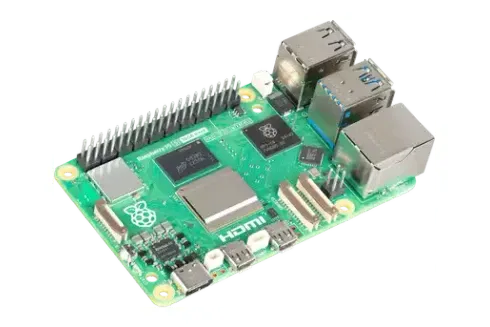
Few pieces of hardware have done more to democratise smart‑home innovation than the pocket‑sized Raspberry Pi. Once aimed purely at teaching coding fundamentals, this single‑board computer has matured into a flexible command centre that can power lighting, heating, security, and much more-all on a shoestring budget. In this refreshed guide we explore how a Raspberry Pi unlocks creative, secure, and scalable home‑automation workflows for beginners and enthusiasts alike.
Put plainly, the aim here is to unlock the true potential of this tiny powerhouse by exploring hands‑on projects that turn theory into convenient, everyday reality.
Why Choose Raspberry Pi for Home Automation
The sheer popularity of Raspberry Pi in maker circles is not an accident. It blends affordability with surprising processing muscle, plus an ever‑growing ecosystem of hats, sensors, and community‑supported projects. Most importantly, it offers complete ownership of your data and hardware-a stark contrast to many closed, cloud‑first smart‑home hubs.
Stand‑out Advantages
- Low cost, high value: Even the latest models cost a fraction of purpose‑built hubs while delivering comparable performance.
- Open platform: With full access to the Linux shell you can tweak, update, and repair your system at will.
- Thriving community: Tutorials, forums, and ready‑made images shorten the learning curve dramatically.
- Modular expansion: GPIO pins and USB ports invite experimentation with sensors, relays, and Zigbee or Z‑Wave radios.
Because of these traits the Raspberry Pi often becomes the beating heart of an evolving smart‑home network rather than a disposable gadget you replace each upgrade cycle.
Planning Your Pi‑Powered Smart Home
Before you solder wires or flash an SD card, spend time mapping out what you want the system to achieve. Clear goals save both money and frustration.
Define Your Core Objectives
Ask yourself which daily pain points automation should ease: Do you want lights that follow sunrise and sunset? A thermostat that learns your schedule? Cameras that notify you only when a human-not the cat-wanders past? Listing priorities guides hardware purchases and keeps your codebase tidy.
Select the Right Model
A Raspberry Pi 4 B or newer handles multiple high‑definition camera feeds, real‑time voice control, and secure VPN access without breaking a sweat. Older zero‑class boards excel at single‑purpose tasks such as water‑leak detection or mailbox alerts. Mixing models gives you redundancy while spreading the workload.
Building the Foundation: Operating Systems & Frameworks
Your choice of software stack will influence performance, maintenance effort, and future flexibility.
Popular Choices
Home Assistant OS remains the community favourite thanks to its slick dashboard and 2,000‑plus integrations. OpenHAB trades ease for granular rule scripting, while Node‑RED appeals to visual thinkers who prefer drag‑and‑drop logic flows. Whichever route you pick, keep daily backups on a second SD card or network share.
Setting Up Reliable Connectivity
Smart‑home gear fails if the network wobbles. Hard‑wire the Raspberry Pi to your router via Ethernet whenever possible. If Wi‑Fi is unavoidable, use the 5 GHz band for lower interference and configure static IP addresses so integrations never lose track of the hub.
Quick Checklist
- Update firmware (
sudo rpi‑update) after the first boot. - Change default passwords and disable unused services.
- Assign a fixed IP or reserve one on the router.
- Generate SSH keys for password‑free yet secure remote access.
Following this list now prevents headaches later.
Connecting Devices the Smart Way
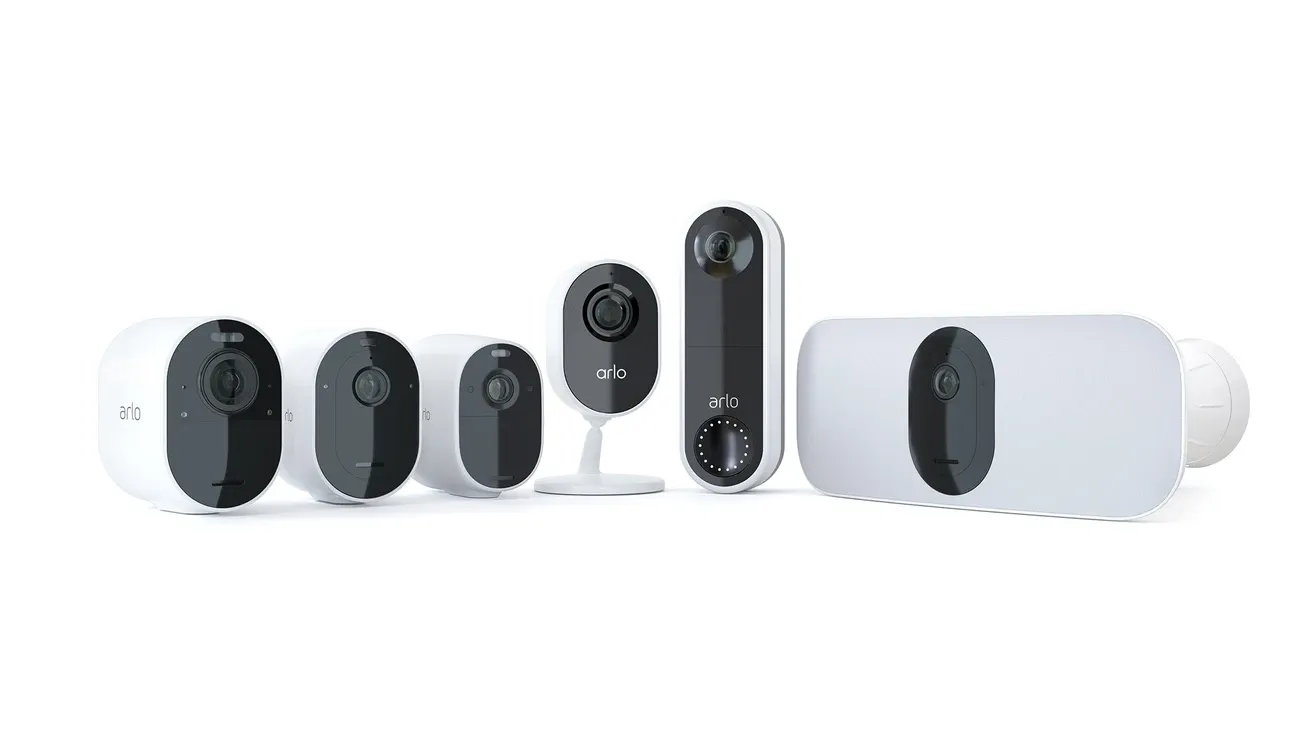
Most homeowners start with lighting, because visual feedback makes success obvious. Pairing Philips Hue bulbs through Zigbee2MQTT or Z‑Wave switches via a USB dongle gives instant, local control without relying on corporate servers. From there, branch into sensors that report temperature, humidity, motion, or luminosity, letting your Raspberry Pi react in real time.
One Hub, Many Protocols
A single Raspberry Pi can juggle Bluetooth Low Energy, Wi‑Fi, Zigbee, Z‑Wave, and even 433 MHz RF if you attach the right radios. Consolidating protocols minimises latency and keeps automations inside your own four walls.
Automating Everyday Routines
automation is not just about turning things on and off; it is about weaving technology invisibly into life.
- Morning scene: As the bedroom sensor notes movement, blinds rise gradually, gentle white LEDs fade up, and your favourite playlist starts in the kitchen.
- Away mode: When all residents leave the geofence, thermostats drop a few degrees and indoor cameras arm themselves.
- Energy guard: If power usage spikes beyond a set threshold, heavy appliances pause until off‑peak hours.
Such routines cut bills, boost security, and reclaim mental space because the house simply does the right thing for you.
Securing Your Smart‑Home Nucleus
Running critical infrastructure on any computer demands diligence. Regularly patch the OS, enforce strong passwords, and consider a firewall such as UFW or iptables. For sensitive devices-door locks or alarm sirens-place them on a separate VLAN where guest gadgets cannot snoop. Finally, encrypt backups so household data stays private even if a drive ends up in the wrong hands.
Expanding Possibilities with Add‑ons
The fun rarely stops at basic lighting and heating. Add a USB TV tuner to record broadcasts, a passive‑PoE hat to cut cable clutter, or an AI accelerator like Google Coral for lightning‑fast person detection in CCTV streams. Because a Raspberry Pi runs standard Linux, almost any maker‑grade accessory can bolt on with minimal tweaks.
Final Thoughts
A decade ago, crafting a bespoke smart‑home system required expensive proprietary controllers. Today, a palm‑sized Raspberry Pi offers the same-often superior-capabilities while respecting your wallet and your privacy. Start small, iterate often, and let curiosity drive your next automation. With patience and a dash of ingenuity, you will find that the only real limit is your imagination. The flexibility and control that Raspberry Pi provides make it an ideal foundation for anyone serious about building a truly customized smart home experience.
The Raspberry Pi community continues to grow and evolve, bringing new possibilities to home automation enthusiasts around the world. Whether you are just beginning your smart home journey or looking to upgrade an existing system, the Raspberry Pi offers unmatched versatility and value. Its open source nature means you always have access to the latest developments and can customize every aspect of your setup to match your specific needs and preferences. This level of control is simply not available with most commercial smart home solutions.
As hardware advances and software frameworks mature, the gap between professional installations and hobbyist builds continues to narrow. Many households now run Raspberry Pi setups that rival expensive proprietary systems in reliability and feature depth. With each new generation of the board, processing power improves while energy consumption remains modest, making the Raspberry Pi an ideal choice for always‑on automation hubs that run quietly in a closet or behind a monitor.