Open source smart home platforms give users complete transparency and control over how their connected devices operate. Unlike proprietary ecosystems that lock you into specific hardware or cloud services, open source solutions let you inspect the code, modify behavior, and contribute improvements back to the community. This approach resonates strongly with privacy-conscious homeowners and technically skilled enthusiasts.
Projects built on open source foundations benefit from rapid innovation driven by thousands of contributors worldwide. Bug fixes arrive quickly, new device integrations appear regularly, and documentation improves continuously through community collaboration. The result is software that evolves faster than most commercial alternatives while remaining free to use.
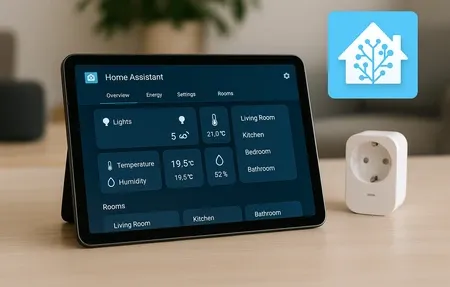
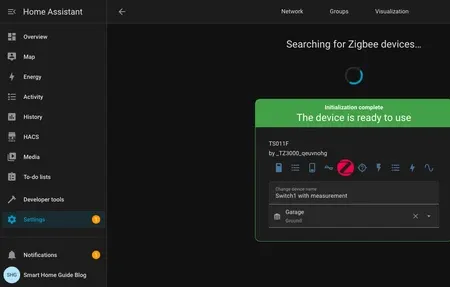
Building a smart home with open source tools typically starts with selecting a central platform. Popular choices include systems that run on affordable hardware like single-board computers or repurposed desktops. These platforms support hundreds of device protocols including Zigbee, Z-Wave, Thread, and plain WiFi, providing broad compatibility without requiring expensive proprietary hubs.
The DIY nature of open source smart homes means you can customize every aspect of your setup. Create complex automation rules using visual editors or scripting languages. Design custom dashboards tailored to your household needs. Integrate with third-party services through well-documented APIs. The only limit is your imagination and willingness to learn.
Community forums and documentation repositories provide extensive support for newcomers. Step-by-step installation guides, video tutorials, and troubleshooting threads help flatten the learning curve. Many users find that the initial investment in learning pays dividends through a more reliable, private, and capable smart home system.
Data ownership stands as one of the strongest arguments for choosing open source home automation. Every sensor reading, automation log, and usage pattern stays on hardware you control. There are no subscription fees for accessing your own data, no risk of a company shutting down its cloud service, and no concern about third parties analyzing your household habits for advertising purposes.
Interoperability between different manufacturers and protocols is a core strength of community-driven platforms. Open source developers write and maintain integrations for thousands of devices from hundreds of brands. When a new product launches, community members often create support within days rather than waiting months for official firmware updates from the manufacturer.
Testing and experimentation become much easier with open source tools. You can run a development instance alongside your production setup, try new integrations without risking your working configuration, and roll back changes instantly if something breaks. This flexibility encourages learning and helps users build increasingly sophisticated automation systems over time.
Cost efficiency improves significantly when you choose open source platforms for home automation. The software itself is free, and it runs on inexpensive hardware that most technology enthusiasts already own. Compared to proprietary systems that require specific hubs, monthly subscriptions, and vendor-locked accessories, an open source approach can deliver equivalent or superior functionality at a fraction of the long-term cost.
Plugin architectures in popular open source platforms allow developers to extend functionality without modifying core code. This modular design means that specialized features like advanced energy monitoring, machine learning based presence detection, or sophisticated lighting scenes can be added independently. Users install only the components they need, keeping their system lean and maintainable.
Reliability tends to increase with open source smart home setups because local processing eliminates dependency on external servers. Internet outages do not disable your lights, locks, or climate controls. Automations continue running on schedule regardless of network conditions. This resilience makes open source platforms particularly attractive for critical home functions like security monitoring and temperature regulation.
The educational value of working with open source home automation should not be underestimated. Users develop practical skills in networking, programming, system administration, and electronics through hands-on projects. These skills transfer directly to professional technology careers, making smart home tinkering both a productive hobby and a valuable learning experience.
Version control and configuration management practices from software development apply directly to open source smart home maintenance. Storing automation rules, device configurations, and integration settings in structured files means every change is tracked, reversible, and shareable. Teams of household members can collaborate on home automation improvements just as developers collaborate on code projects.
Long-term sustainability favors open source platforms because community-maintained software does not disappear when a single company changes strategy. Proprietary smart home products frequently lose cloud support after a few years, rendering expensive hardware useless. Open source alternatives continue receiving updates as long as users find them valuable, with development responsibility distributed across a global network of contributors rather than dependent on one organization's business decisions.